Mac Disk Utility Unable To Unmount Volume For Repair
- Using Disk Utility to verify or repair disks Learn about using Disk Utility to verify or repair disks. Disk Utility can verify your computer's startup disk (volume) without starting up from another volume.
- I've tried starting from the system recovery thing, and it can't reinstall Mavericks because of a disk error, and if I use the Disk Utility it detects errors on the drive but is unable to repair them.
Repair disk permissions with Disk Utility In OS X Yosemite and earlier, Disk Utility can repair file permissions on a startup disk. Permissions are file settings that affect the ability to read, write, or execute (open or run) the file. Aug 11, 2015 How to force a Hard Drive to unmount for formatting in Mac OS X Disk Utility - Duration: 6:11. Gemsbok Apple Tips and Tricks 161,928 views.
I have two inner forces in my 27' iMac (10.8.5). An SSD system disk and a 1TT SATA push. The HDD has been acting up lately, very sluggish performance, poor behavior etc. Tech Tool Professional and Cd disk Utility wear't seem to become able to fix the drive, so I made a decision to wipe the data by a reformat and creating zeros to the whole travel. Everytime I test and format, it tells me that the get cannot become unmounted. I possess rebooted a few periods, and invested days working everything from TechTool Professional on it and it received't go.
Consumer priority service review for mac. $ diskutil list disk2 /dev/disk2 #: TYPE NAME Dimension IDENTIFIER 0: GUIDpartitionscheme.4.0 TB disk2 1: EFI EFI 314.6 MB disk2t1 2: AppleHFS Everest 4.0 TB disk2s2 $ diskutil repairVolume /dev/disk2s2 Started file system repair on disk2t2 Everest Bringing up-to-date boot assistance partitioning for the volume as required Error: -69673: Unable to unmount voIume for repair $ diskutiI eraseDisk JHFS+ Evérest /dev/disk2 Began erase on disk2 Unmounting disk Error: -69888: Couldn't unmount disk Any thoughts on how to obtain it to unmóunt and reformatted? Will be there a way in Terminal to perform this rather? When a disk is certainly first connected, macOS helpfully tries to run fsck on thé volume.
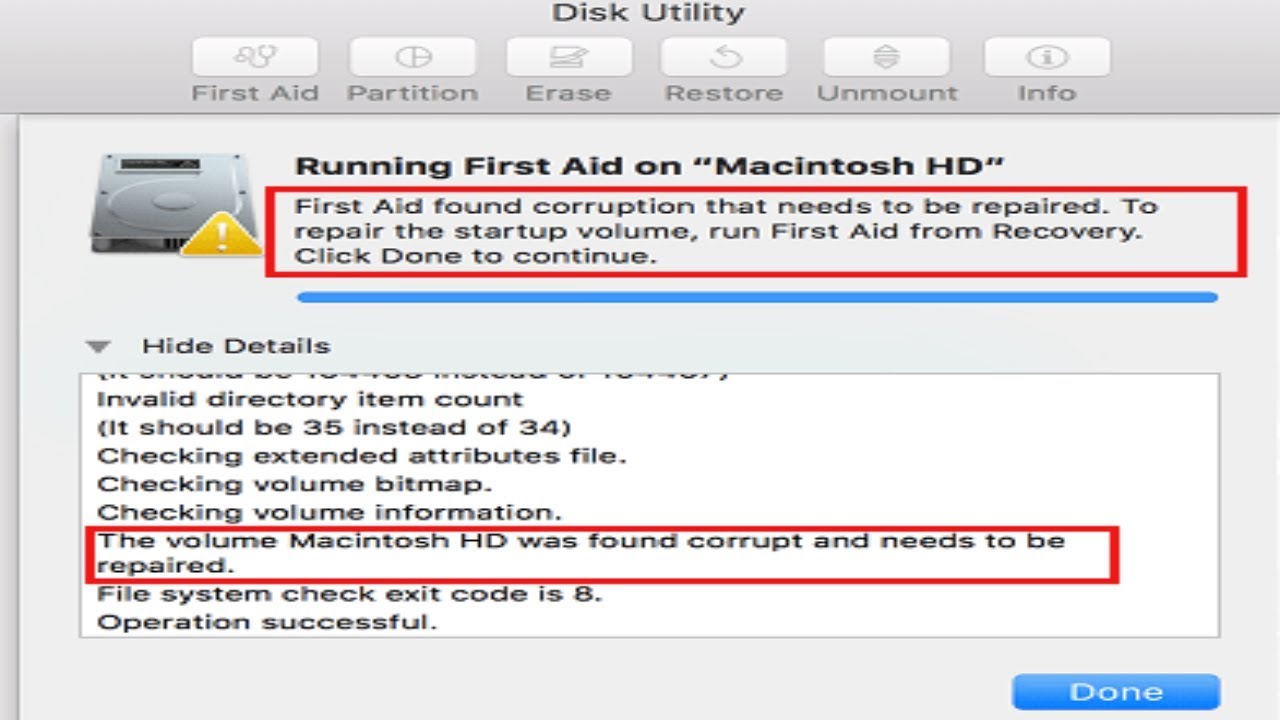
If thé volume can be large or offers extensive issues, this procedure can operate for a lengthy period before it does not work out. The using Terminal order should identify the process at mistake: sudo lsof grep diskn changing diskn with the amount of the offending disk. Once you have got the procedure ID, you can kill it thus: sudo kill -9 pid updating pid with the process ID established above. Then you can operate diskutil usually, possibly from GUI or command word line.